I want to tell you straight off what this story is about: Sometime in the next 40 years, robots are going to take your job.
I don’t care what your job is. If you dig ditches, a robot will dig them better. If you’re a magazine writer, a robot will write your articles better. If you’re a doctor, IBM’s Watson will no longer “assist” you in finding the right diagnosis from its database of millions of case studies and journal articles. It will just be a better doctor than you.
Until we figure out how to fairly distribute the fruits of robot labor, it will be an era of mass joblessness and mass poverty.
And CEOs? Sorry. Robots will run companies better than you do. Artistic types? Robots will paint and write and sculpt better than you. Think you have social skills that no robot can match? Yes, they can. Within 20 years, maybe half of you will be out of jobs. A couple of decades after that, most of the rest of you will be out of jobs.
In one sense, this all sounds great. Let the robots have the damn jobs! No more dragging yourself out of bed at 6 a.m. or spending long days on your feet. We’ll be free to read or write poetry or play video games or whatever we want to do. And a century from now, this is most likely how things will turn out. Humanity will enter a golden age.
But what about 20 years from now? Or 30? We won’t all be out of jobs by then, but a lot of us will—and it will be no golden age. Until we figure out how to fairly distribute the fruits of robot labor, it will be an era of mass joblessness and mass poverty. Working-class job losses played a big role in the 2016 election, and if we don’t want a long succession of demagogues blustering their way into office because machines are taking away people’s livelihoods, this needs to change, and fast. Along with global warming, the transition to a workless future is the biggest challenge by far that progressive politics—not to mention all of humanity—faces. And yet it’s barely on our radar.
That’s kind of a buzzkill, isn’t it? Luckily, it’s traditional that stories about difficult or technical subjects open with an entertaining or provocative anecdote. The idea is that this allows readers to ease slowly into daunting material. So here’s one for you: Last year at Christmas, I was over at my mother’s house and mentioned that I had recently read an article about Google Translate. It turns out that a few weeks previously, without telling anyone, Google had switched over to a new machine-learning algorithm. Almost overnight, the quality of its translations skyrocketed. I had noticed some improvement myself but had chalked it up to the usual incremental progress these kinds of things go through. I hadn’t realized it was due to a quantum leap in software.
But if Google’s translation algorithm was better, did that mean its voice recognition was better too? And its ability to answer queries? Hmm. How could we test that? We decided to open presents instead of cogitating over this.
But after that was over, the subject of erasers somehow came up. Which ones are best? Clear? Black? Traditional pink? Come to think of it, why are erasers traditionally pink? “I’ll ask Google!” I told everyone. So I pulled out my phone and said, “Why are erasers pink?” Half a second later, Google told me.

Not impressed? You should be. We all know that phones can recognize voices tolerably well these days. And we know they can find the nearest café or the trendiest recipe for coq au vin. But what about something entirely random? And not a simple who, where, or when question. This was a why question, and it wasn’t about why the singer Pink uses erasers or why erasers are jinxed. Google has to be smart enough to figure out in context that I said pink and that I’m asking about the historical reason for the color of erasers, not their health or the way they’re shaped. And it did. In less than a second. With nothing more than a cheap little microprocessor and a slow link to the internet.
(In case you’re curious, Google got the answer from Design*Sponge: “The eraser was originally produced by the Eberhard Faber Company…The erasers featured pumice, a volcanic ash from Italy that gave them their abrasive quality, along with their distinctive color and smell.”)
Still not impressed? When Watson famously won a round of Jeopardy! against the two best human players of all time, it needed a computer the size of a bedroom to answer questions like this. That was only seven years ago.
What do pink erasers have to do with the fact that we’re all going to be out of a job in a few decades? Consider: Last October, an Uber trucking subsidiary named Otto delivered 2,000 cases of Budweiser 120 miles from Fort Collins, Colorado, to Colorado Springs—without a driver at the wheel. Within a few years, this technology will go from prototype to full production, and that means millions of truck drivers will be out of a job.
Automated trucking doesn’t rely on newfangled machines, like the powered looms and steam shovels that drove the Industrial Revolution of the 19th century. Instead, like Google’s ability to recognize spoken words and answer questions, self-driving trucks—and cars and buses and ships—rely primarily on software that mimics human intelligence. By now everyone’s heard the predictions that self-driving cars could lead to 5 million jobs being lost, but few people understand that once artificial-intelligence software is good enough to drive a car, it will be good enough to do a lot of other things too. It won’t be millions of people out of work; it will be tens of millions.
This is what we mean when we talk about “robots.” We’re talking about cognitive abilities, not the fact that they’re made of metal instead of flesh and powered by electricity instead of chicken nuggets.
Unfortunately, for those of us worried about robots taking away our jobs, these advances mean that mass unemployment is a lot closer than we feared—so close, in fact, that it may be starting already.
In other words, the advances to focus on aren’t those in robotic engineering—though they are happening, too—but the way we’re hurtling toward artificial intelligence, or AI. While we’re nowhere near human-level AI yet, the progress of the past couple of decades has been stunning. After many years of nothing much happening, suddenly robots can play chess better than the best grandmaster. They can play Jeopardy! better than the best humans. They can drive cars around San Francisco—and they’re getting better at it every year. They can recognize faces well enough that Welsh police recently made the first-ever arrest in the United Kingdomusing facial recognition software. After years of plodding progress in voice recognition, Google announced earlier this year that it had reduced its word error rate from 8.5 percent to 4.9 percent in 10 months.
All of this is a sign that AI is improving exponentially, a product of both better computer hardware and software. Hardware has historically followed a growth curve called Moore’s law, in which power and efficiency double every couple of years, and recent improvements in software algorithms have been even more explosive. For a long time, these advances didn’t seem very impressive: Going from the brainpower of a bacterium to the brainpower of a nematode might technically represent an enormous leap, but on a practical level it doesn’t get us that much closer to true artificial intelligence. However, if you keep up the doubling for a while, eventually one of those doubling cycles takes you from the brainpower of a lizard (who cares?) to the brainpower of a mouse and then a monkey (wow!). Once that happens, human-level AI is just a short step away.
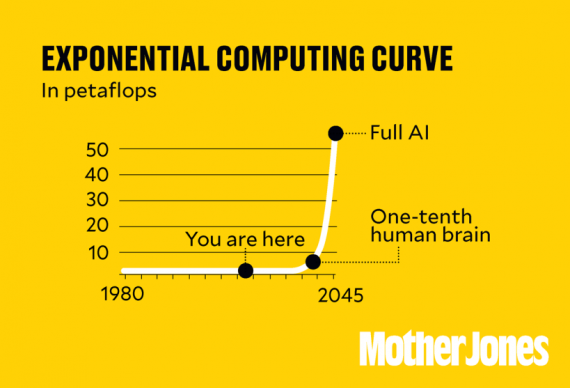
This can be hard to imagine, so here’s a chart that shows what an exponential doubling curve looks like, measured in petaflops (quadrillions of calculations per second). During the first 70 years of the digital era, computing power doubled every couple of years—and that produced steadily improving accounting software, airplane reservation systems, weather forecasts, Spotify, and the like. But on the scale of the human brain—usually estimated at 10 to 50 petaflops—it produced computing power so minuscule that you can’t see any change at all. Around 2025 we’ll finally start to see visible progress toward artificial intelligence. A decade later we’ll be up to about one-tenth the power of a human brain, and a decade after that we’ll have full human-level AI. It will seem like it happened overnight, but it’s really the result of a century of steady—but mostly imperceptible—progress.
Are we really this close to true AI? Here’s a yardstick to think about. Even with all this doubling going on, until recently computer scientists thought we were still years away from machines being able to win at the ancient game of Go, usually regarded as the most complex human game in existence. But last year, a computer beat a Korean grandmaster considered one of the best of all time, and earlier this year it beat the highest-ranked Go player in the world. Far from slowing down, progress in artificial intelligence is now outstripping even the wildest hopes of the most dedicated AI cheerleaders. Unfortunately, for those of us worried about robots taking away our jobs, these advances mean that mass unemployment is a lot closer than we feared—so close, in fact, that it may be starting already. But you’d never know that from the virtual silence about solutions in policy and political circles.
I’m hardly alone in thinking we’re on the verge of an AI Revolution. Many who work in the software industry—people like Bill Gates and Elon Musk—have been sounding the alarm for years. But their concerns are largely ignored by policymakers and, until recently, often ridiculed by writers tasked with interpreting technology or economics. So let’s take a look at some of the most common doubts of the AI skeptics.
#1: We’ll never get true AI because computing power won’t keep doubling forever. We’re going to hit the limits of physics before long. There are several pretty good reasons to dismiss this claim as a roadblock. To start, hardware designers will invent faster, more specialized chips. Google, for example, announced last spring that it had created a microchip called a Tensor Processing Unit, which it claimed was up to 30 times faster and 80 times more power efficient than an Intel processor for machine learning tasks. A huge array of those chips are now available to researchers who use Google’s cloud services. Other chips specialized for specific aspects of AI (image recognition, neural networking, language processing, etc.) either exist already or are certain to follow.
What’s more, this raw power is increasingly being harnessed in a manner similar to the way the human brain works. Your brain is not a single, superpowerful computing device. It’s made up of about 100 billion neurons working in parallel—i.e., all at the same time—to create human-level intelligence and consciousness. At the lowest level, neurons operate in parallel to create small clusters that perform semi-independent actions like responding to a specific environmental cue. At the next level, dozens of these clusters work together in each of about 100 “sub-brains”—distinct organs within the brain that perform specialized jobs such as speech, visual processing, and balance. Finally, all these sub-brains operate in parallel, and the resulting overall state is monitored and managed by executive functions that make sense of the world and provide us with our feeling that we have conscious control of our actions.
Modern computers also yoke lots of microprocessors together. As of 2017, the fastest computer in the world uses roughly 40,000 processors with 260 cores each. That’s more than 10 million processing cores running in parallel. Each one of these cores has less power than the Intel processor on your desktop, but the entire machine delivers about the same power as the human brain.
This doesn’t mean AI is here already. Far from it. This “massively parallel” architecture still presents enormous programming challenges, but as we get better at exploiting it we’re certain to make frequent breakthroughs in software performance. In other words, even if Moore’s law slows down or stops, the total power of everything put together—more use of custom microchips, more parallelism, more sophisticated software, and even the possibility of entirely new ways of doing computing—will almost certainly keep growing for many more years.
#2: Even if computing power keeps doubling, it has already been doubling for decades. You guys keep predicting full-on AI, but it never happens. It’s true that during the early years of computing there was a lot of naive optimism about how quickly we’d be able to build intelligent machines. But those rosy predictions died in the ’70s, as computer scientists came to realize that even the fastest mainframes of the day produced only about a billionth of the processing power of the human brain. It was a humbling realization, and the entire field has been almost painfully realistic about its progress ever since.
We’ve finally built computers with roughly the raw processing power of the human brain—although only at a cost of more than $100 million and with an internal architecture that may or may not work well for emulating the human mind. But in another 10 years, this level of power will likely be available for less than $1 million, and thousands of teams will be testing AI software on a platform that’s actually capable of competing with humans.
#3: Okay, maybe we will get full AI. But it only means that robots will act intelligent, not that they’ll really be intelligent. This is just a tedious philosophical debating point. For the purposes of employment, we don’t really care if a smart computer has a soul—or if it can feel love and pain and loyalty. We only care if it can act like a human being well enough to do anything we can do. When that day comes, we’ll all be out of jobs even if the computers taking our places aren’t “really” intelligent.
#4: Fine. But waves of automation—steam engines, electricity, computers—always lead to predictions of mass unemployment. Instead they just make us more efficient. The AI Revolution will be no different. This is a popular argument. It’s also catastrophically wrong.
The Industrial Revolution was all about mechanical power: Trains were more powerful than horses, and mechanical looms were more efficient than human muscle. At first, this did put people out of work: Those loom-smashing weavers in Yorkshire—the original Luddites—really did lose their livelihoods. This caused massive social upheaval for decades until the entire economy adapted to the machine age. When that finally happened, there were as many jobs tending the new machines as there used to be doing manual labor. The eventual result was a huge increase in productivity: A single person could churn out a lot more cloth than she could before. In the end, not only were as many people still employed, but they were employed at jobs tending machines that produced vastly more wealth than anyone had thought possible 100 years before. Once labor unions began demanding a piece of this pie, everyone benefited.
They will manufacture themselves, program themselves, repair themselves, and manage themselves. If you don’t appreciate this, then you don’t appreciate what’s barreling toward us.
The AI Revolution will be nothing like that. When robots become as smart and capable as human beings, there will be nothing left for people to do because machines will be both stronger and smarter than humans. Even if AI creates lots of new jobs, it’s of no consequence. No matter what job you name, robots will be able to do it. They will manufacture themselves, program themselves, repair themselves, and manage themselves. If you don’t appreciate this, then you don’t appreciate what’s barreling toward us.
In fact, it’s even worse. In addition to doing our jobs at least as well as we do them, intelligent robots will be cheaper, faster, and far more reliable than humans. And they can work 168 hours a week, not just 40. No capitalist in her right mind would continue to employ humans. They’re expensive, they show up late, they complain whenever something changes, and they spend half their time gossiping. Let’s face it: We humans make lousy laborers.
If you want to look at this through a utopian lens, the AI Revolution has the potential to free humanity forever from drudgery. In the best-case scenario, a combination of intelligent robots and green energy will provide everyone on Earth with everything they need. But just as the Industrial Revolution caused a lot of short-term pain, so will intelligent robots. While we’re on the road to our Star Trek future, but before we finally get there, the rich are going to get richer—because they own the robots—and the rest of us are going to get poorer because we’ll be out of jobs. Unless we figure out what we’re going to do about that, the misery of workers over the next few decades will be far worse than anything the Industrial Revolution produced.
Wait, wait, skeptics will say: If all this is happening as we speak, why aren’t people losing their jobs already? Several sharp observers have made this point, including James Surowiecki in a recent issue of Wired. “If automation were, in fact, transforming the US economy,” he wrote, “two things would be true: Aggregate productivity would be rising sharply, and jobs would be harder to come by than in the past.” But neither is happening. Productivity has actually stalled since 2000 and jobs have gotten steadily more plentiful ever since the Great Recession ended. Surowiecki also points out that job churn is low, average job tenure hasn’t changed much in decades, and wages are rising—though he admits that wage increases are “meager by historical standards.”
Mass unemployment is closer than we feared—in fact, it may be starting already.
True enough. But as I wrote four years ago, since 2000 the share of the population that’s employed has decreased; middle-class wages have flattened; corporations have stockpiled more cash and invested less in new products and new factories; and as a result of all this, labor’s share of national income has declined. All those trends are consistent with job losses to old-school automation, and as automation evolves into AI, they are likely to accelerate.
That said, the evidence that AI is currently affecting jobs is hard to assess, for one big and obvious reason: We don’t have AI yet, so of course we’re not losing jobs to it. For now, we’re seeing only a few glimmers of smarter automation, but nothing even close to true AI.
Remember that artificial intelligence progresses in exponential time. This means that even as computer power doubles from a trillionth of a human brain’s power to a billionth and then a millionth, it has little effect on the level of employment. Then, in the relative blink of an eye, the final few doublings take place and robots go from having a thousandth of human brainpower to full human-level intelligence. Don’t get fooled by the fact that nothing much has happened yet. In another 10 years or so, it will.
So let’s talk about which jobs are in danger first. Economists generally break employment into cognitive versus physical jobs and routine versus nonroutine jobs. This gives us four basic categories of work:
Routine physical: digging ditches, driving trucks
Routine cognitive: accounts-payable clerk, telephone sales
Nonroutine physical: short-order cook, home health aide
Nonroutine cognitive: teacher, doctor, CEO
Routine tasks will be the first to go—and thanks to advances in robotics engineering, both physical and cognitive tasks will be affected. In a recent paper, a team from Oxford and Yale surveyed a large number of machine-learning researchers to produce a “wisdom of crowds” estimate of when computers would be able to take over various human jobs. Two-thirds said progress in machine learning had accelerated in recent years, with Asian researchers even more optimistic than North American researchers about the advent of full AI within 40 years.
But we don’t need full AI for everything. The machine-learning researchers estimate that speech transcribers, translators, commercial drivers, retail sales, and similar jobs could be fully automated during the 2020s. Within a decade after that, all routine jobs could be gone.
Nonroutine jobs will be next: surgeons, novelists, construction workers, police officers, and so forth. These jobs could all be fully automated during the 2040s. By 2060, AI will be capable of performing any task currently done by humans. This doesn’t mean that literally every human being on the planet will be jobless by then—in fact, the researchers suggest it could take another century before that happens—but that’s hardly any solace. By 2060 or thereabouts, we’ll have AI that can do anything a normal human can do, which means that nearly all normal jobs will be gone. And normal jobs are what almost all of us have.
2060 seems a long way off, but if the Oxford-Yale survey is right, we’ll face an employment apocalypse far sooner than that: the disappearance of routine work of all kinds by the mid-2030s. That represents nearly half the US labor force. The consulting firm PricewaterhouseCoopers recently released a study saying much the same. It predicts that 38 percent of all jobs in the United States are “at high risk of automation” by the early 2030s, most of them in routine occupations. In the even nearer term, the World Economic Forum predicts that the rich world will lose 5 million jobs to robots by 2020, while a group of AI experts, writing in Scientific American, figures that 40 percent of the 500 biggest companies will vanish within a decade.
Not scared yet? Kai-Fu Lee, a former Microsoft and Google executive who is now a prominent investor in Chinese AI startups, thinks artificial intelligence “will probably replace 50 percent of human jobs.” When? Within 10 years. Ten years!Maybe it’s time to really start thinking hard about AI.
And forget about putting the genie back in the bottle. AI is coming whether we like it or not. The rewards are just too great. Even if America did somehow stop AI research, it would only mean that the Chinese or the French or the Brazilians would get there first. Russian President Vladimir Putin agrees. “Artificial intelligence is the future, not only for Russia but for all humankind,” he announced in September. “Whoever becomes the leader in this sphere will become the ruler of the world.” There’s just no way around it: For the vast majority of jobs, work as we know it will come steadily to an end between about 2025 and 2060.
So who benefits? The answer is obvious: the owners of capital, who will control most of the robots. Who suffers? That’s obvious too: the rest of us, who currently trade work for money. No work means no money.
But things won’t actually be quite that grim. After all, fully automated farms and factories will produce much cheaper goods, and competition will then force down prices. Basic material comfort will be cheap as dirt.
Still not free, though. And capitalists can only make money if they have someone to sell their goods to. This means that even the business class will eventually realize that ubiquitous automation doesn’t really benefit them after all. They need customers with money if they want to be rich themselves.
Why Elon Musk Is Sounding the Alarm on Artificial Intelligence
One way or another, then, the answer to the mass unemployment of the AI Revolution has to involve some kind of sweeping redistribution of income that decouples it from work. Or a total rethinking of what “work” is. Or a total rethinking of what wealth is. Let’s consider a few of the possibilities.
The welfare state writ large: This is the simplest to think about. It’s basically what we have now, but more extensive. Unemployment insurance will be more generous and come with no time limits. National health care will be free for all. Anyone without a job will qualify for some basic amount of food and housing. Higher taxes will pay for it, but we’ll still operate under the assumption that gainful employment is expected from anyone able to work.
This is essentially the “bury our heads in the sand” option. We refuse to accept that work is truly going away, so we continue to punish people who aren’t employed. Jobless benefits remain stingy so that people are motivated to find work—even though there aren’t enough jobs to go around. We continue to believe that eventually the economy will find a new equilibrium.
This can’t last for too long, and millions will suffer during the years we continue to delude ourselves. But it will protect the rich for a while.
Universal basic income #1: This is a step further down the road. Everyone would qualify for a certain level of income from the state, but the level of guaranteed income would be fairly modest because we would still want people to work. Unemployment wouldn’t be as stigmatized as it is in today’s welfare state, but neither would widespread joblessness be truly accepted as a permanent fact of life. Some European countries are moving toward a welfare state with cash assistance for everyone.
Universal basic income #2: This is UBI on steroids. It’s available to everyone, and the income level is substantial enough to provide a satisfying standard of living. This is what we’ll most likely get once we accept that mass unemployment isn’t a sign of lazy workers and social decay, but the inevitable result of improving technology. Since there’s no personal stigma attached to joblessness and no special reason that the rich should reap all the rewards of artificial intelligence, there’s also no reason to keep the universal income level low. After all, we aren’t trying to prod people back into the workforce. In fact, the time will probably come when we actively want to do just the opposite: provide an income large enough to motivate people to leave the workforce and let robots do the job better.
Silicon Valley—perhaps unsurprisingly—is fast becoming a hotbed of UBI enthusiasm. Tech executives understand what’s coming, and that their own businesses risk a backlash unless we take care of its victims. Uber has shown an interest in UBI. Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg supports it. Ditto for Tesla CEOElon Musk and Slack CEO Stewart Butterfield. A startup incubator called Y Combinator is running a pilot program to find out what happens if you give people a guaranteed income.
There are even some countries that are now trying it. Switzerland rejected a UBI proposal in 2016, but Finland is experimenting with a small-scale UBI that pays the unemployed about $700 per month even after they find work. UBI is also getting limited tryouts by cities in Italy and Canada. Right now these are all pilot projects aimed at learning more about how to best run a UBI program and how well it works. But as large-scale job losses from automation start to become real, we should expect the idea to spread rapidly.
A tax on robots: This is a notion raised by a draft report to the European Parliament and endorsed by Bill Gates, who suggests that robots should pay income tax and payroll tax just like human workers. That would keep humans more competitive. Unfortunately, there’s a flaw here: The end result would be to artificially increase the cost of employing robots, and thus the cost of the goods they produce. Unless every country creates a similar tax, it accomplishes nothing except to push robot labor overseas. We’d be worse off than if we simply let the robots take our jobs in the first place. Nonetheless, a robot tax could still have value as a way of modestly slowing down job losses. Economist Robert Shiller suggests that we should consider “at least modest robot taxes during the transition to a different world of work.” And where would the money go? “Revenue could be targeted toward wage insurance,” he says. In other words, a UBI.
Socialization of the robot workforce: In this scenario, which would require a radical change in the US political climate, private ownership of intelligent robots would be forbidden. The market economy we have today would continue to exist with one exception: The government would own all intelligent robots and would auction off their services to private industry. The proceeds would be divided among everybody.
Progressive taxation on a grand scale: Let the robots take all the jobs, but tax all income at a flat 90 percent. The rich would still have an incentive to run businesses and earn more money, but for the most part labor would be considered a societal good, like infrastructure, not the product of individual initiative.
Wealth tax: Intelligent robots will be able to manufacture material goods and services cheaply, but there will still be scarcity. No matter how many robots you have, there’s only so much beachfront property in Southern California. There are only so many original Rembrandts. There are only so many penthouse suites. These kinds of things will be the only real wealth left, and the rich will still want them. So if robots make the rich even richer, they’ll bid up the price of these luxuries commensurately, and all that’s left is to tax them at high rates. The rich still get their toys, while the rest of us get everything we want except for a view of the sun setting over the Pacific Ocean.
A hundred years from now, all of this will be moot. Society will adapt in ways we can’t foresee, and we’ll all be far wealthier, safer, and more comfortable than we are today—assuming, of course, that the robots don’t kill us all, Skynet fashion.
But someone needs to be thinking hard about how to prepare for what happens in the meantime. Not many are. Last year, for example, the Obama White House released a 48-page report called “Preparing for the Future of Artificial Intelligence.” That sounds promising. But it devoted less than one page to economic impacts and concluded only that “policy questions raised by AI-driven automation are important but they are best addressed by a separate White House working group.”
Regrettably, the coming jobocalypse has so far remained the prophecy of a few Cassandras: mostly futurists, academics, and tech executives. For example, Eric Schmidt, chairman of Google’s parent company, believes that AI is coming faster than we think, and that we should provide jobs to everyone during the transition. “The country’s goal should be full employment all the time, and do whatever it takes,” he says.
Another sharp thinker about our jobless future is Martin Ford, author of Rise of the Robots. Mass joblessness, he warns, isn’t limited to low-skill workers. Nor is it something we can fight by committing to better education. AI will decimate any job that’s “predictable”—which means nearly all of them. Many of us might not like to hear this, but Ford is unsentimental about the work we do. “Relatively few people,” he says, are paid “primarily to engage in truly creative work or ‘blue sky’ thinking.”

Either liberals start working on an answer now, or voters will rally around a more dangerous demagogue than Trump.
Nonetheless, somebody on the left with numbers, clout, power, and organizing energy—hopefully all the above—had better start. Conventional wisdom says Trump’s victory last year was tipped over the edge by a backlash among working-class voters in the Upper Midwest. When blue-collar workers start losing their jobs in large numbers, we’ll see a backlash that makes 2016 look like a gentle breeze. Either liberals start working on answers now, or we risk voters rallying around far more effective and dangerous demagogues than Trump.
Despite the amount of media attention that both robots and AI have gotten over the past few years, it’s difficult to get people to take them seriously. But start to pay attention and you see the signs: An Uber car can drive itself. A computer can write simple sports stories. SoftBank’s Pepper robot already works in more than 140 cellphone stores in Japan and is starting to get tryouts in America too. Alexa can order replacement Pop-Tarts before you know you need them. A Carnegie Mellon computer that seems to have figured out human bluffing beat four different online-poker pros earlier this year. California, suffering from a lack of Mexican workers, is ground zero for the development of robotic crop pickers. Sony is promising a robot that will form an emotional bond with its owner.
These are all harbingers, the way a dropping barometer signals a coming storm—not the possibility of a storm, but the inexorable reality. The two most important problems facing the human race right now are the need for widespread deployment of renewable energy and figuring out how to deal with the end of work. Everything else pales in comparison. Renewable energy already gets plenty of attention, even if half the country still denies that we really need it. It’s time for the end of work to start getting the same attention.
Written by Kevin Drum
Kevin is a political blogger for Mother Jones. Email Kevin [email protected]. For more of his stories, click here or follow him on Facebook.